You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
- Thread starter Daniel E.
- Start date
More threads by Daniel E.
I don't think I have read anything that explains SI urges and the cycle as well as this artical does. As someone who SI's and has many urges, this explains the motions very well.
If we can understand the motions we are going through , hopefully we can learn to catch it as it is happening and hopefully find better ways to cope the SI.
Great artical Daniel. Thank you for finding this and posting it.
If we can understand the motions we are going through , hopefully we can learn to catch it as it is happening and hopefully find better ways to cope the SI.
Great artical Daniel. Thank you for finding this and posting it.
Excerpt from the "cycle of self-injury" chapter in Healing the Hurt Within:
One strategy from DBT is Behavior Chain Analysis.Ultimately though, true healing from self-injury involves coming face-to-face with whatever unresolved internal issues and conflicts are motivating, and maintaining the act. That can be a tall order, as it means ‘sitting with the emotional pain’. However, a willingness and commitment to ‘stick with it and work through it’ can lead to a life-changing and transforming experience for the better, as well as an opportunity to kick self-injury...for ever...
Key points
- Everyone who self-injures is an individual, thus their pattern of self-injury may not follow one typical route.
- Many who self-injure hold negative self-beliefs.
- Trauma triggers (nightmares, flashbacks and body memories [somatic sensations]) can be the catalyst for self-injury episodes.
- Shame and embarrassment may deter the reporting of, or seeking medical help for, internal self-injury.
- The relief from self-injury is usually short-lived.
- Breaking the cycle of self-injury involves facing and working through the issues that are motivating and maintaining the act.
- The motivations and meanings of self-injury are diverse.
Re: How to get rid of suicide thoughts
The Cycle of Self-Injury
by Jan Sutton
[Cycle goes from A to F and then starts again at A as discussed in the author's book Healing the Hurt Within.]
A: MENTAL ANGUISH
Intrusive thoughts, images, flashbacks, body memories (physical sensations), negative self-beliefs, feeling trapped.
A fire starts smoldering
B: EMOTIONAL ENGULFMENT
Smoldering fire sparks powerful feelings and emotions – trigger a raging inferno.
Frightened, desperate, about to explode, or dissociated
C: PANIC STATIONS
The raging inferno gathers momentum. Feeling out of control, too numb (detached, distant, disconnected).
Compelling urge to self-injure
D: ACTION STATIONS
Self-injures, which extinguishes the raging inferno inside, or alleviates the feelings of alienation.
Act may be carried out in a state of:
•Awareness (feels pain)
•Partial awareness (some pain)
•Non-awareness (dissociative)
Act may be motivated by:
•Need to release tension oranxiety
•Need to communicate distress
•Need to feel pain (punish)
•Need to escape from emotional pain (dissociative)
•Need to end dissociative state
•Need to exert sense of control
•Need to ward off suicidal thoughts
E: FEEL BETTER / DIFFERENT
With the raging inferno under control:
•Relief from tension and emotion
•Feeling of euphoria, numbness or detachment
•Sense of feeling more alive, more real, more grounded in reality, or (if motivation was punishment) degree of satisfaction
Generally, feels calmer, more in control, comfortably numb, think more clearly. Self-injury appears to reduce level of emotional and bodily arousal to a tolerable level, and internal chaos is soothed. Physical injuries seem small price to pay to escape from the raging inferno.
F: THE GRIEF REACTION
Reality of actions starts to sink in. Shame, guilt, self-disgust or self-hate may rekindle the smouldering embers.
Because underlying issues remain unresolved, the cycle continues unless change is effected at point A.
The Cycle of Self-Injury
by Jan Sutton
[Cycle goes from A to F and then starts again at A as discussed in the author's book Healing the Hurt Within.]
A: MENTAL ANGUISH
Intrusive thoughts, images, flashbacks, body memories (physical sensations), negative self-beliefs, feeling trapped.
A fire starts smoldering
B: EMOTIONAL ENGULFMENT
Smoldering fire sparks powerful feelings and emotions – trigger a raging inferno.
Frightened, desperate, about to explode, or dissociated
C: PANIC STATIONS
The raging inferno gathers momentum. Feeling out of control, too numb (detached, distant, disconnected).
Compelling urge to self-injure
D: ACTION STATIONS
Self-injures, which extinguishes the raging inferno inside, or alleviates the feelings of alienation.
Act may be carried out in a state of:
•Awareness (feels pain)
•Partial awareness (some pain)
•Non-awareness (dissociative)
Act may be motivated by:
•Need to release tension oranxiety
•Need to communicate distress
•Need to feel pain (punish)
•Need to escape from emotional pain (dissociative)
•Need to end dissociative state
•Need to exert sense of control
•Need to ward off suicidal thoughts
E: FEEL BETTER / DIFFERENT
With the raging inferno under control:
•Relief from tension and emotion
•Feeling of euphoria, numbness or detachment
•Sense of feeling more alive, more real, more grounded in reality, or (if motivation was punishment) degree of satisfaction
Generally, feels calmer, more in control, comfortably numb, think more clearly. Self-injury appears to reduce level of emotional and bodily arousal to a tolerable level, and internal chaos is soothed. Physical injuries seem small price to pay to escape from the raging inferno.
F: THE GRIEF REACTION
Reality of actions starts to sink in. Shame, guilt, self-disgust or self-hate may rekindle the smouldering embers.
Because underlying issues remain unresolved, the cycle continues unless change is effected at point A.
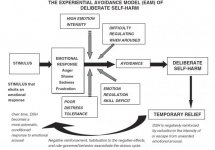
Experiential Avoidance and Emotion Regulation in Borderline Personality Disorder
Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy
January 2011
...The occasional avoidance of unpleasant internal experiences on its own may be relatively inconsequential. Chronic emotional avoidance, however, may be particularly detrimental. Distress experienced by persons with BPD increases their use of EA [emotional avoidance], which in turn increases physiological arousal and subjective distress, and so on. This positive feedback cycle has been conceptualized as the mechanism by which deliberate self-harm is developed and maintained as a coping strategy. According to the Experiential Avoidance Model of self-harm , the act of escaping or avoiding unpleasant emotions through DSH [deliberate self-harm] is reinforced in the short term by relief from emotional arousal. In the long-term, however, escape or avoidance prevents new learning (i.e., through exposure), causes a ??rebound effect,?? and actually increases the probability of more frequent or intense negative experiences. These negative experiences then prompt further emotional avoidance (possibly including deliberate self-harm), and the cycle is strengthened and maintained...
, the act of escaping or avoiding unpleasant emotions through DSH [deliberate self-harm] is reinforced in the short term by relief from emotional arousal. In the long-term, however, escape or avoidance prevents new learning (i.e., through exposure), causes a ??rebound effect,?? and actually increases the probability of more frequent or intense negative experiences. These negative experiences then prompt further emotional avoidance (possibly including deliberate self-harm), and the cycle is strengthened and maintained...
Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy
January 2011
...The occasional avoidance of unpleasant internal experiences on its own may be relatively inconsequential. Chronic emotional avoidance, however, may be particularly detrimental. Distress experienced by persons with BPD increases their use of EA [emotional avoidance], which in turn increases physiological arousal and subjective distress, and so on. This positive feedback cycle has been conceptualized as the mechanism by which deliberate self-harm is developed and maintained as a coping strategy. According to the Experiential Avoidance Model of self-harm
 , the act of escaping or avoiding unpleasant emotions through DSH [deliberate self-harm] is reinforced in the short term by relief from emotional arousal. In the long-term, however, escape or avoidance prevents new learning (i.e., through exposure), causes a ??rebound effect,?? and actually increases the probability of more frequent or intense negative experiences. These negative experiences then prompt further emotional avoidance (possibly including deliberate self-harm), and the cycle is strengthened and maintained...
, the act of escaping or avoiding unpleasant emotions through DSH [deliberate self-harm] is reinforced in the short term by relief from emotional arousal. In the long-term, however, escape or avoidance prevents new learning (i.e., through exposure), causes a ??rebound effect,?? and actually increases the probability of more frequent or intense negative experiences. These negative experiences then prompt further emotional avoidance (possibly including deliberate self-harm), and the cycle is strengthened and maintained...
Replying is not possible. This forum is only available as an archive.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 6K
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 6K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 35K
- Replies
- 15
- Views
- 7K